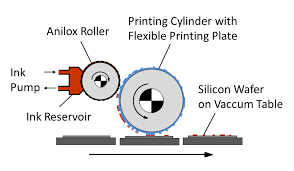
since it is covered with thousands of small wells or cups that enable it to meter ink to the printing plate in a uniform thickness evenly and quickly (the number of cells per linear inch can vary according to the type of print job and the quality required). To avoid getting a final product with a smudgy or lumpy look, it must be ensured that the amount of ink on the printing plate is not excessive. This is achieved by using a scraper, called a doctor blade. The doctor blade removes excess ink from the anilox roller before inking the printing plate. The substrate is finally sandwiched between the plate and the impression cylinder to transfer the image. The sheet is then fed through a dryer, which allows the inks to dry before the surface is touched again.
Flexo has an advantage over lithography in that it can use a wider range of inks, water based rather than oil based inks, and is good at printing on a variety of different materials like plastic, foil, acetate film, brown paper, and other materials used in packaging. Typical products printed using flexography include brown corrugated boxes, flexible packaging including retail and shopping bags, food and hygiene bags and sacks, milk and beverage cartons, flexible plastics, self-adhesive labels, disposable cups and containers, envelopes and wallpaper. In recent years there has also been a move towards laminates, where two or more materials are bonded together to produce new material with different properties than either of the originals. Flexographic inks, like those used in gravure and unlike those used in lithography, generally have a low viscosity. This enables faster drying and, as a result, faster production, which results in lower costs.
Printing press speeds of up to 600 meters per minute (2000 feet per minute) are achievable now with modern technology high-end printers. Flexographic printing is widely used in the converting industry for printing plastic materials for packaging and other end uses. For maximum efficiency, the flexo presses produce large rolls of material that are then slit down to their finished size on slitting machines.